Basic Electronics for Beginners in 20 Steps
Step 9: Transistors
A transistor takes a small electrical current at its base pin and amplifies it, allowing a larger current to pass between the collector and emitter pins. The current passing between these two pins is proportional to the voltage applied at the base pin.
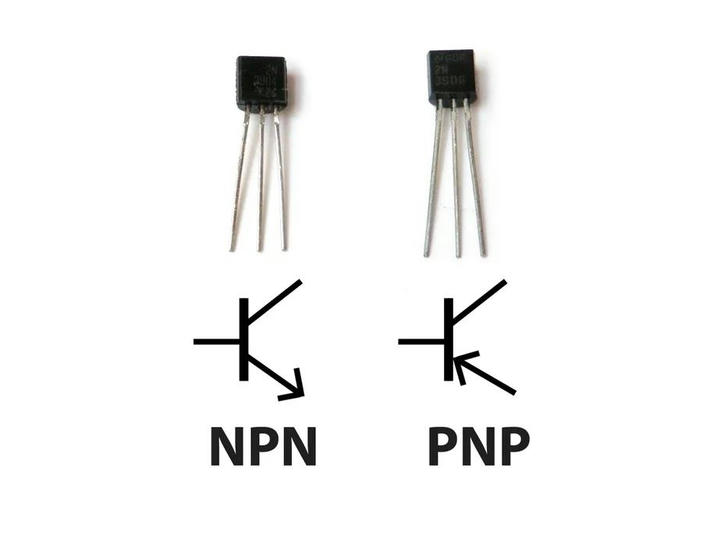
There are two basic types of transistors: NPN and PNP, which have opposite polarities between the collector and emitter.
NPN transistors allow current to flow from the collector to the emitter. In schematics, they’re represented with a line for the base, a diagonal line connected to the base, and an arrow pointing away from the base.
PNP transistors allow current to flow from the emitter to the collector. They’re represented similarly, but the arrow points towards the base instead.
Transistors have part numbers printed on them, and you can look up their datasheets to learn about their pin layouts and specific properties, including voltage and current ratings.
